Customer Churn Modeling & Retention Optimization with SparkML, MLflow, & Neural Networks
This project focuses on predicting customer churn for a telecommunications provider serving more than 7,000 home phone and internet customers. The goal is to flag high-risk customers early and give the business enough lead time to intervene with targeted retention offers.
I built a baseline Logistic Regression model to provide interpretable churn probabilities, then extended the work with a multi-layer neural network in TensorFlow and a scalable SparkML + MLflow pipeline in Databricks. Together, these implementations demonstrate how to move from exploratory churn analysis to production-ready modeling and experiment tracking.
Background & Problem Statement
In subscription businesses like telecom, retaining existing customers is far more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. However, churn drivers are often complex, spanning pricing, service quality, contract terms, and customer demographics. Without data-driven insight, retention programs can be scattered and inefficient.
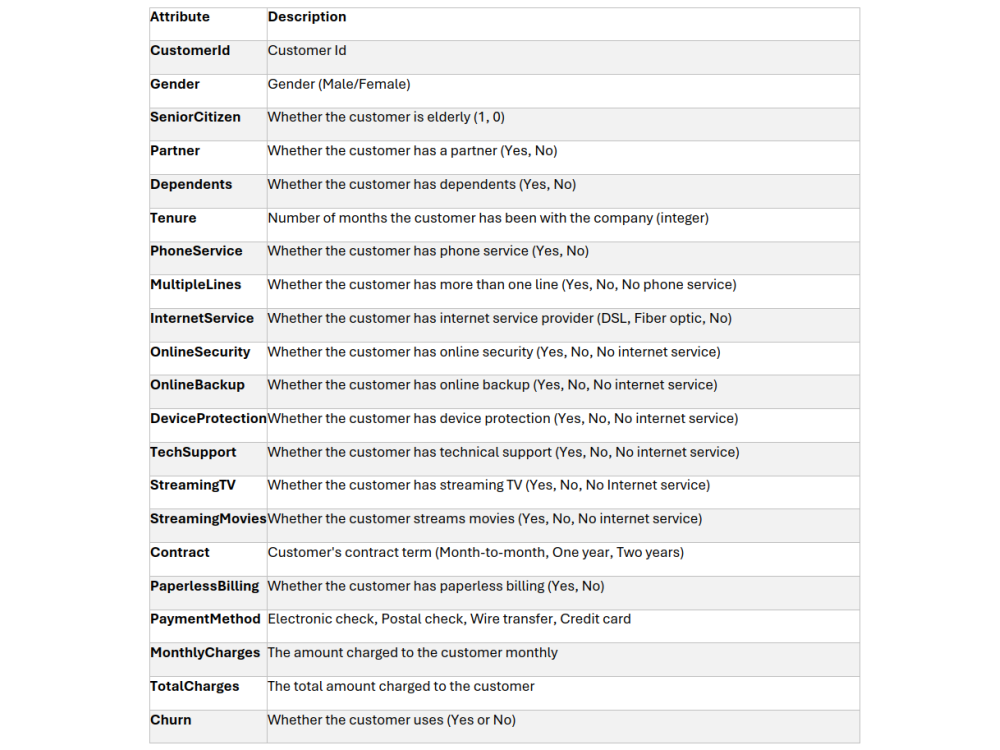
The telco dataset used in this project includes customer demographics (age, dependents, partner), service details (phone, internet, streaming, technical support), contract and billing information (month-to-month vs. annual, paperless billing, payment method), and a churn label indicating whether each customer left within the past month.
Problem Statement: How can we use modern machine learning techniques to predict which telecom customers are most likely to churn, and translate those predictions into actionable retention strategies that prioritize high-value, high-risk segments?
Model Development
The modeling workflow combined careful data preprocessing, exploratory analysis, and multiple ML approaches—including Logistic Regression, Neural Networks, and a SparkML production pipeline.
- Data Understanding: The dataset captured demographic and service attributes such as gender, senior citizen status, dependents, tenure, phone and internet service, streaming and tech-support options, contract length, payment method, monthly charges, and total charges, along with a binary churn label.
- Exploratory Findings: Early analysis revealed that many customers who churn do so within their first month of service, and that churn risk is substantially higher for customers paying $70–$110 per month on month-to-month contracts compared with lower-paying or longer-term customers.
- Preprocessing & Feature Engineering: Categorical variables were encoded into numeric form, continuous variables were cleaned and standardized as needed, and the data was shuffled and split into 80% training and 20% testing sets with stratification by churn label to preserve class proportions.
- Class Imbalance Handling: Because churners form a minority class, both resampling techniques (SMOTE) and probability-threshold tuning strategies were evaluated to improve recall on the churn class while controlling false positives.
Two core modeling approaches were developed on the processed dataset:
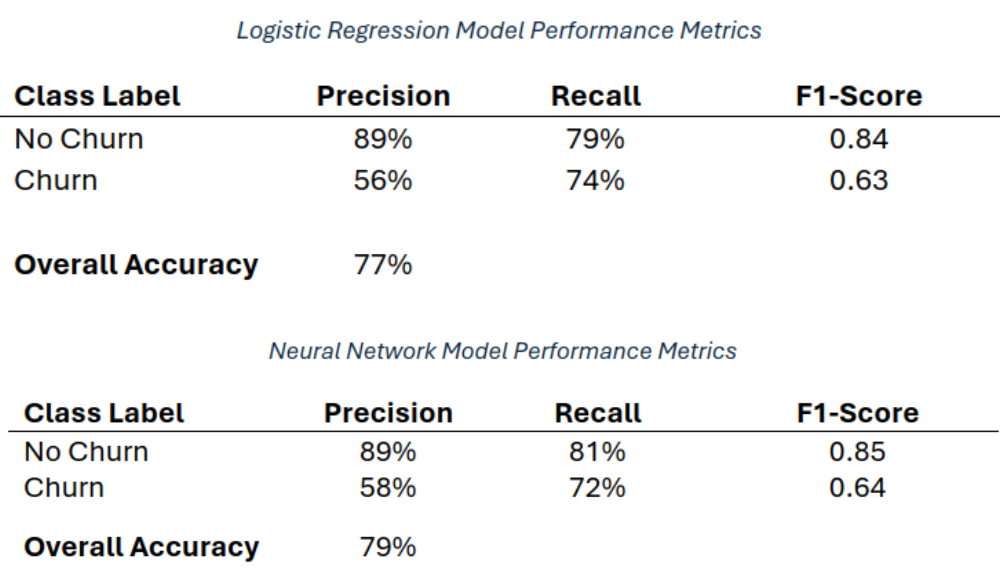
- Logistic Regression (Baseline): A Logistic Regression model was trained to estimate churn probabilities and provide interpretable coefficients for each feature. On the held-out test set, the model achieved an overall accuracy of around 77%, with strong performance on both churn and non-churn classes (e.g., churn F1 score in the low 0.60s, non-churn F1 in the mid 0.80s).
- Neural Network (TensorFlow): A feedforward neural network with one input layer, three hidden layers, and a sigmoid output was trained on the same feature set. The neural net achieved slightly higher overall accuracy (~79%) and marginal improvements in macro F1, demonstrating that both interpretable linear models and deeper architectures can effectively capture churn patterns.
SparkML, Databricks & MLflow Deployment
To demonstrate a production-oriented implementation, the project was extended into a Databricks environment using SparkML and MLflow. This version is designed for large-scale, iterative churn modeling on real customer tables.
- Data Ingestion: Customer records were stored as a managed Databricks table, with Spark handling distributed loading and preprocessing across the cluster.
- SparkML Pipeline: A Logistic Regression model was implemented as a SparkML pipeline, including feature indexing/encoding, vector assembly, and model training—mirroring the structure of the earlier Python/scikit-learn implementation but at production scale.
- MLflow Experiment Tracking: MLflow was used to track experiments, hyperparameters, metrics, and model artifacts, enabling side-by-side comparison of different feature configurations, regularization strengths, and decision thresholds.
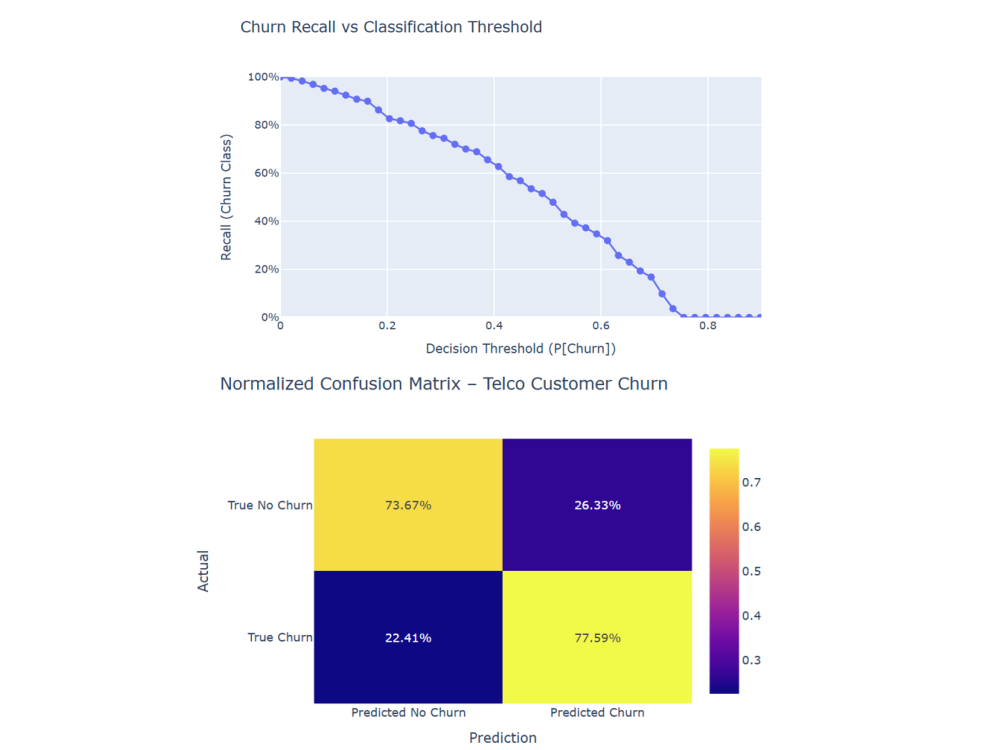
- Threshold Optimization: To address class imbalance, the default 0.5 decision threshold was tuned toward the baseline churn rate (~26%). This improved churn recall from roughly 50% to about 78%, giving the business greater visibility into at-risk customers at the cost of a controlled increase in false positives.
- Interactive Analysis: Plotly-based visualizations were integrated to explore precision–recall trade-offs, ROC curves, and churn-risk distribution across customer segments.
Impact & Actionable Insights
The combined modeling and deployment workflow delivers not just predictions, but concrete levers for improving retention strategy and marketing efficiency.
- Targeted Retention Offers: Model results show that customers on month-to-month contracts with monthly charges above ~$70 are significantly more likely to churn. These customers become prime candidates for introductory discounts, bundled services, or incentives to switch to longer-term contracts.
- Early-Lifecycle Interventions: Many churn events occur during the first month of service, suggesting the need for stronger onboarding, proactive support, and early feedback loops for new customers.
- Explainable Drivers of Churn: Logistic Regression provides interpretable coefficients, clearly linking churn risk to attributes like contract length, tenure, and billing method. These insights can be shared directly with marketing and customer-success teams.
- Scalable MLOps Template: The Databricks + SparkML + MLflow implementation serves as a reusable template for other subscription-based businesses, enabling them to plug in their own customer tables, retrain, and monitor churn models in a production environment.
- Balanced Performance: By carefully tuning class imbalance handling and decision thresholds, the models strike a practical balance between catching at-risk customers and minimizing unnecessary retention spend.